The following examples walk through using chkptstanr
with the popular R package brms.
The basic idea is to (1) generate the Stan
code with brms, (2) fit the model with cmdstanr (with
the desired number of checkpoints), and then (3) return a
brmsfit object. This is all done internally, so the
workflow is very similar to using brms.
Example 1: No Stopping
Model Fitting
You can use chkpt_brms in nearly the same way as brm. The only difference is that you need to specify the path to the folder where the checkpoints will be stored, and the number of iterations between each checkpoint.
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy')When running the above, a custom progress bar is printed that includes information about the checkpoints.
#> Initial Warmup (Typical Set)
#> Chkpt: 1 / 10; Iteration: 200 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 2 / 10; Iteration: 400 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 3 / 10; Iteration: 600 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 4 / 10; Iteration: 800 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 5 / 10; Iteration: 1000 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 6 / 10; Iteration: 1200 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 7 / 10; Iteration: 1400 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 8 / 10; Iteration: 1600 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 9 / 10; Iteration: 1800 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 10 / 10; Iteration: 2000 / 2000 (sample)
Checkpointing completeIn this case, checkpointing is complete.
Summary
fit1 is a brmsfit object which means that
all of the functionality of brms can still be used.
Here is the summary output:
Family: poisson
Links: mu = log
Formula: count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1 | patient)
Data: data (Number of observations: 236)
Draws: 4 chains, each with iter = 2000; warmup = 1000; thin = 1;
total post-warmup draws = 4000
Multilevel Hyperparameters:
~patient (Number of levels: 59)
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
sd(Intercept) 0.58 0.07 0.45 0.73 1.00 956 1696
Regression Coefficients:
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
Intercept 1.77 0.12 1.53 2.00 1.00 887 1575
zAge 0.10 0.09 -0.07 0.26 1.00 871 1256
zBase 0.70 0.12 0.47 0.94 1.00 986 1675
Trt1 -0.26 0.16 -0.60 0.05 1.01 987 1170
zBase:Trt1 0.05 0.16 -0.26 0.37 1.00 1075 1824
Draws were sampled using sample(hmc). For each parameter, Bulk_ESS
and Tail_ESS are effective sample size measures, and Rhat is the potential
scale reduction factor on split chains (at convergence, Rhat = 1).Posterior Predictive Check
Of course, due to being a brmsfit object, it is seamless
perform a posterior predictive check.
pp_check(fit1)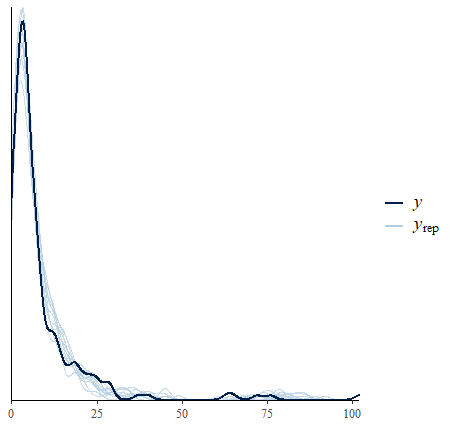
Example 2: Stoping, restarting, and resetting
We can interupt the sampling manually:
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy')
#> Compiling Stan program...
#> Initial Warmup (Typical Set)
#> Chkpt: 1 / 10; Iteration: 200 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 2 / 10; Iteration: 400 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 3 / 10; Iteration: 600 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 4 / 10; Iteration: 800 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 5 / 10; Iteration: 1000 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 6 / 10; Iteration: 1200 / 2000 (sample)
#> Sampling aborted. You can examine the results or continue sampling by rerunning the same code.If the sampler is passed the warmup stage, it returns a
brmsfit object, so you can examine the results:
summary(fit1) Family: poisson
Links: mu = log
Formula: count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1 | patient)
Data: data (Number of observations: 236)
Draws: 4 chains, each with iter = 1200; warmup = 1000; thin = 1;
total post-warmup draws = 800
Multilevel Hyperparameters:
~patient (Number of levels: 59)
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
sd(Intercept) 0.57 0.07 0.45 0.72 1.02 209 236
Regression Coefficients:
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
Intercept 1.75 0.11 1.52 1.98 1.02 206 371
zAge 0.10 0.08 -0.07 0.25 1.02 240 443
zBase 0.70 0.11 0.47 0.95 1.00 220 370
Trt1 -0.24 0.16 -0.56 0.07 1.02 199 239
zBase:Trt1 0.05 0.15 -0.26 0.35 1.00 243 350
Draws were sampled using sample(hmc). For each parameter, Bulk_ESS
and Tail_ESS are effective sample size measures, and Rhat is the potential
scale reduction factor on split chains (at convergence, Rhat = 1).We see that the model has not converged, and we can continue sampling by rerunning the same code.
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy')
#> Model executable is up to date!
#> Chkpt: 7 / 10; Iteration: 1400 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 8 / 10; Iteration: 1600 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 9 / 10; Iteration: 1800 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 10 / 10; Iteration: 2000 / 2000 (sample)
#> Checkpointing completeAnd examine the final results:
summary(fit1)Family: poisson
Links: mu = log
Formula: count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1 | patient)
Data: data (Number of observations: 236)
Draws: 4 chains, each with iter = 2000; warmup = 1000; thin = 1;
total post-warmup draws = 4000
Multilevel Hyperparameters:
~patient (Number of levels: 59)
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
sd(Intercept) 0.58 0.07 0.45 0.73 1.00 956 1696
Regression Coefficients:
Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
Intercept 1.77 0.12 1.53 2.00 1.00 887 1575
zAge 0.10 0.09 -0.07 0.26 1.00 871 1256
zBase 0.70 0.12 0.47 0.94 1.00 986 1675
Trt1 -0.26 0.16 -0.60 0.05 1.01 987 1170
zBase:Trt1 0.05 0.16 -0.26 0.37 1.00 1075 1824Predetermine stopping point
In addition to manually aborting the run, we can predetermine the
stopping point by specifying the number of iterations after which to
stop the sampler via the stop_after argument.
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
stop_after = 1400,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy')
#> Compiling Stan program...
#> Initial Warmup (Typical Set)
#> Chkpt: 1 / 10; Iteration: 200 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 2 / 10; Iteration: 400 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 3 / 10; Iteration: 600 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 4 / 10; Iteration: 800 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 5 / 10; Iteration: 1000 / 2000 (warmup)
#> Chkpt: 6 / 10; Iteration: 1200 / 2000 (sample)
#> Chkpt: 7 / 10; Iteration: 1400 / 2000 (sample)
#> Sampling aborted. You can examine the results or continue sampling by rerunning the same code.Reset sampling
If we want to reset the sampling, we can use the reset
argument, as long as we have not changed any of the key arguments. For
example, we can reset the sampling and start from scratch, but we cannot
change the formula, data, or family (but we can change “stop_after”)
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ zAge + zBase * Trt + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy',
stop_after = 1600,
reset = TRUE)If we try to change the formula, data, or family, we will get an error:
fit1 <- chkpt_brms(count ~ 1 + (1|patient),
data = epilepsy,
family = poisson(),
iter_per_chkpt = 200,
path = 'checkpoints/epilepsy',
stop_after = 1600,
reset = TRUE)Error: Important arguments have been changed. Please completely reset the checkpointing via reset_checkpoints(path, recompile = TRUE).
Interupted before or during warmup. No samples available.This is because we cannot use the existing compiled model. We need to reset the checkpoints and recompile the model:
reset_checkpoints('checkpoints/epilepsy', recompile = TRUE)